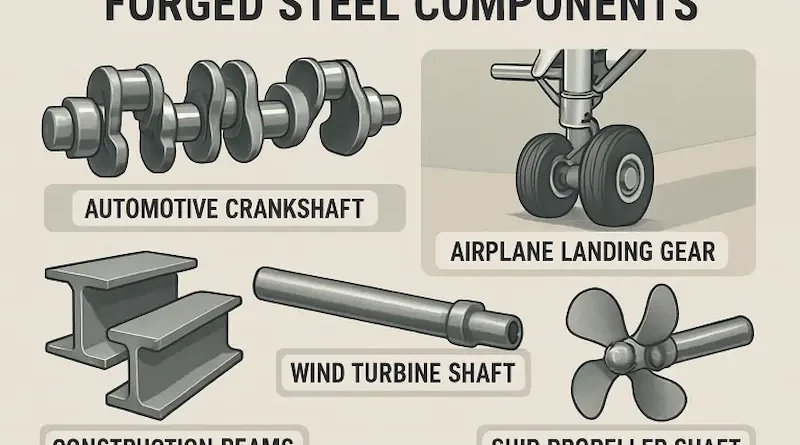
Innovative Applications of Forged Steel in Modern Industries
Forged steel remains a backbone of technological advancement, thanks to its superb mechanical strength and resilience. Today, industries ranging from automotive to medical are evolving by harnessing next-generation forged steel solutions. As performance demands increase, so do expectations for sustainability, longevity, and efficiency—all of which forged steel delivers as a material. Whether it’s shaping the mobility of tomorrow or supporting groundbreaking infrastructure, innovations in forging are making a remarkable impact. For organizations seeking both expertise and reliable components, a trusted forged steel valve manufacturer can play a crucial role in project success.
The adoption of digital technologies and eco-friendly practices is redefining how forged steel is produced and applied. From AI-driven maintenance to advancements in alloy development, industries are creating stronger, lighter, and greener products. These constant improvements are helping organizations meet increasingly stringent standards for both safety and sustainability, while driving new growth opportunities.
Automotive Industry
Forged steel components drive innovation in automotive engineering, particularly with the emergence of electric vehicles (EVs) and the adoption of lightweighting strategies. Manufacturers rely on forged steel for its superior strength and fatigue resistance in critical engine and drivetrain parts, such as crankshafts and connecting rods. Lightweight, high-strength forged aluminum and steel parts are replacing heavier components, thereby directly contributing to improved fuel efficiency and enhanced performance. Noteworthy innovations include next-generation EV chassis parts, achieving up to 30% weight reduction without sacrificing durability.
Aerospace Sector
Aerospace advancements rely on the reliability and precision of forged steel components, which are used in engines, fuselage structures, and landing gear. The industry now leverages specialized high-strength alloys, including titanium and nickel-based compounds, forged to deliver unprecedented fatigue resistance and weight savings. According to Azom, new forging techniques enable these parts to withstand the extreme thermal and mechanical stresses encountered in flight, thereby increasing both efficiency and passenger safety.
Construction and Infrastructure
Construction and infrastructure developments rely on robust, weather-resistant forged steel for critical structural elements. Columns, beams, and fasteners made from forged steel are vital for the long-term durability of high-rise buildings, bridges, and transportation facilities. Weathering steel is one significant innovation, forming a stable oxide layer that reduces both maintenance costs and corrosion risk. These forged components underpin the strength and longevity of global infrastructure, ensuring projects can withstand decades of environmental stress.
Energy Sector
The energy sector relies on forged steel’s capacity to withstand severe conditions in power plants, pipelines, and drilling environments. Components such as high-pressure turbine shafts, valves, and structural parts for wind turbines are forged to deliver unmatched resistance to fatigue, corrosion, and high temperatures. Recent developments include hydrogen-compatible forged steels, designed for use in next-generation clean energy applications. These materials enable energy suppliers to embrace the shift towards renewables and higher efficiency while maintaining system integrity.
Marine Industry
Shipbuilding and marine engineering demand components that can survive extreme corrosion and mechanical loads. Forged steel forms the backbone of crucial ship parts, such as propeller shafts, anchor chains, and rudder assemblies, ensuring vessels remain durable and safe during extended service in corrosive saltwater environments. These robust supplies ensure both safety and operational reliability for commercial and military fleets worldwide.
Medical Equipment
Medical equipment manufacturing relies heavily on forged steel, due to its unparalleled blend of biocompatibility, strength, and sterilization resistance. Surgical tools, orthopedic implants, and diagnostic devices leverage precision-forged steel to guarantee patient safety and device longevity. The material’s adaptability supports the industry’s ongoing quest for higher standards in health and performance.
Advancements in Forging Technology
Recent years have seen the integration of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and automation across forging operations. AI monitors every production phase, driving quality control and predicting necessary maintenance to reduce both costs and downtime. Additive manufacturing (3D printing) is also transforming how dies and component prototypes come to life, reducing lead times and enhancing precision. The digitalization of the forging process leads to more intelligent factories and faster innovations that can reshape multiple sectors.
Sustainable Practices in Steel Forging
Environmental stewardship is an emerging priority for the steel forging industry. Technologies such as induction heating, which offer up to 50% reductions in energy consumption, are replacing inefficient, gas-fueled systems. Near-net-shape forging and recycling initiatives cut down waste, while AI predictive systems extend the lifespan of expensive equipment. As policy and market forces drive companies toward lower emissions and circular consumption, these sustainable practices become key differentiators.
Forged steel’s enduring properties—strength, resilience, and versatility—remain vital as industries transform towards smarter, more sustainable designs. With ongoing innovations and a focus on eco-friendly practices, forged steel stands at the forefront of modern material solutions, shaping the industries of today and tomorrow.
Visit the rest of the site for more interesting and useful articles.